Atlas 2K 16-bit RISC Processor Core

Details
Category: Processor
Created: March 13, 2013
Updated: January 27, 2020
Language: VHDL
Other project properties
Development Status: Beta
Additional info: FPGA proven, Specification done
WishBone compliant: Yes
WishBone version: n/a
License: GPL
Description
Welcome to the Atlas Processor Core project!
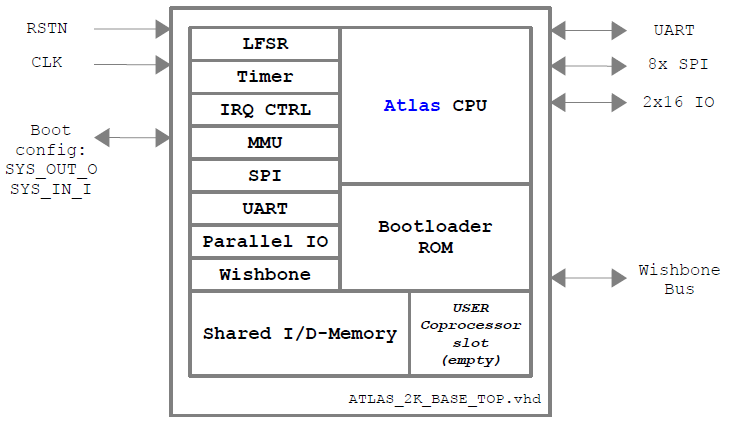
The Atlas 2k Processor is intended to be a small 16-bit RISC general purpose processor for all kind of applications, that require minimal hardware resources while providing a maximum functionality and processing power. The instruction set was inspired by famous architectures like the ARM and AVR ISAs and many of you, who worked with these architectures, will see the resemblance. However, the CPU features a lot of additional nice features and functionalites, which - at least from my point of view - make a cool processor. 😉 The processor supports a flexible memory layout (with paging) and features several common communication interfaces (like SPI, UART and a Wishbone bus adapter) and peripheral devices like timer, interrupt controller and LFSR. An integrated bootloader (2kB ROM) allows to select between several boot options (configuration via 2 external pins):
|
 |
,
,For more information about this project, take a look at the processor documentary: ,Atlas 2k Processor Documentary,
,
,
,
,
Processor Features
- True 16-bit RISC open source soft-core processor, 16-bit processing data, 16-bit memory addressing
- Small outline
- Completely written in behavioral, platform-independent VHDL
- Pipelined instruction execution in 5 stages with full forwarding and hazard detection
- Single cycle execution of all instructions (except for branches and multi-cycle (memory) operations)
- Powerful memory access and indexing instructions
- Two different operating modes with unique register sets (8x 16-bit registers each) and privileges
- Full hardware support for emulating privileged-mode programs in unprivileged-mode
- Two software interrupts/exceptions (system call, command error (instruction access violation))
- Powerful bit-manipulation operations
- Integrated bootloader providing several boot options and functionalities
- Boot from UART / SPI EEPROM / internal memory / Wishbone device
- Program SPI EEPROM
- RAM dump of any memory page
- Dump words from Wishbone network
- Interface for external coprocessors to extend the processor's functionality
- Simple memory and coprocessor interface
- Assembler program to easily create and assemble application code
- Integrated peripheral controller:
- High precision timer (32-bit)
- Memory management unit (supports paging) - 32 bit address space
- Flexible linear-feedback shift register (taps configurable) for pseudo random data
- Internal interrupt controller for up to 8 channels
- 16+8 bit parallel input and 16+8 bit parallel output ports
- General purpose SPI controller with variable transfer frame size, 8 individual channels
- Configurable universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART)
- Wishbone bus master adapter (32-bit address, 16-bit data, pipelined burst transfer, packet size 1..32 16-bit words)
,
,
Programmer Model
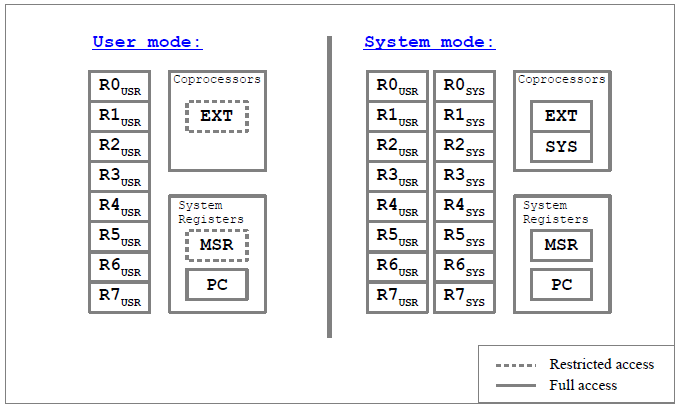 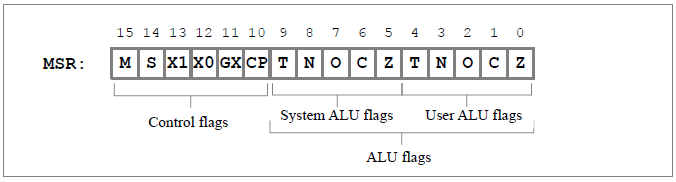 |
ARM thubb-like instruction set. All instructions are 16 bit wide. Arithmetical instructions use 3-register-addressing. The CPU provides two different privilige modes: A privileged one (system mode) and an unprivileged one (user mode). Each mode has access to a register bank of 8x 16-bit register. When operating in system mode, data can also be transfered from or to the user register bank. R7 of each bank is used as link register to store the return address when calling subroutines User mode and system mode programs can access the program counter (PC) and the machine status register (MSR). The PC can be altered by both operating modes. System mode programs have full access to the MSR, but user mode programs can only alter the user ALU flags of the MSR, so an user mode program cannot alter the state of the host system. Both operations mode have also private sets of ALU status flags, so no context store at all is necessary when changing modes. When in system mode, the internal coprocesor and the optional external user processor can be accessed. When in user mode, only the external user processor can be accessed, but however, this access privilege can be deactivated, allowing only system mode programs to have access to the two coprocessor. Five interrupt/execption vectors are supported: 0: Hardware reset, 1: interrupt via the critical IRQ pin, 2: interrupt from the internal IRQ controller (supports another 8 IRQ channels), 3: command error trap, 4: software interrupt (system call). All instructions, that require system privileges, will cause an software interrupt when executed in user mode, allowing hardware-based emulation of system-mode programs in restricted user mode environment. |
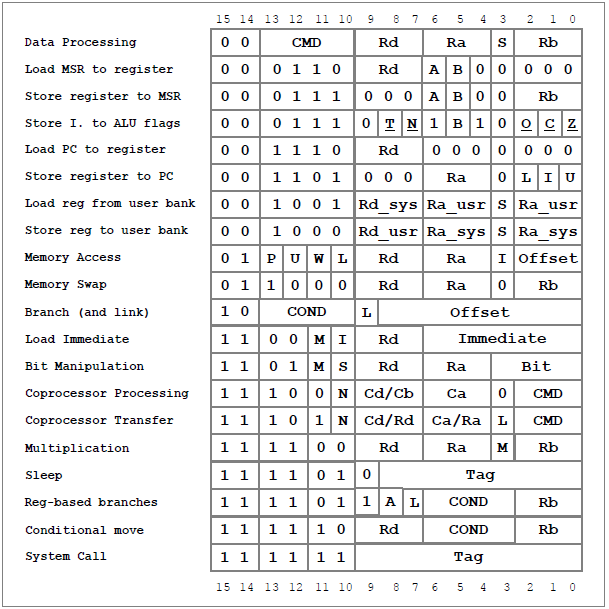
| I have tried to design the instruction set architecture as orthogonal as possible. All data processing instructions (arithmetical, logical, bit manipulation, transfer, ...) can be applied on any of the current mode's 8 data registers. All instructions of these classes feature three operand slots, making the Atlas CPU a three address-machine. For all arithmetical/logical instructions, the update of the status flags is optional. Data memory accesses can be performend unsig any register as pointer/data and as source/destination. Immediate and register-based offset addition/subtraction before or after the actual memory access is possible (pointer indexing). Also, a write back of a modified base address can be enabled. An application-specific coprocessor (EXTernal USER coprocessor) can be connected to the CPU to extend the core's functionality and processing power. Dedicated coprocessor transfer and data processing instructions are supported. The CPU features a power-saving sleep mode. Any enabled interrupt signal will wake up the CPU again (single cycle response time). Single cycle 32-bit multiplier. Instructions to get upper/lower 16-bit multiplication result. Conditional/unconditional immediate branch/call instructions can jump to a location within +255 and -256 instructions. Also, conditional relative/absolute register-based branches are implemented. The newest version also includes conditional register move instructions to accelerate conditional data transfer. For more details about the implemented instructions, see the Atlas 2k Processor Documentary. |
 |
,
,
,
Synthesis Results
Synthesis (speed optimized) results for a Xilinx Spartan XC3S400A FPGA:
| Xilinx Spartan XC3S400A | Atlas 2k Processor Base Setup* |
|---|---|
| Number of Slices: | 1347 / 3584 = 37% |
| Number of 4 input LUTs: | 2406 / 7168 = 33% |
| Number of Slice Flip Flops: | 1091 / 7168 = 15% |
| Number of IOs: | 18 |
| Number of BRAMs: | 11 / 20 = 55% |
| Number of MULT18X18SIOs: | 1 / 20 = 5% |
| Maximum Frequency: | 81.252 MHz |
,
,
,balanced optimization, slow 1200mV 0C model,
,
,
| Altera Cyclone IV EP4CE22F17C6N | Atlas 2k Processor Base Setup* |
|---|---|
| Total logic elements: | 2967 / 22320 = 13% |
| Total combinational functions: | 2692 / 22320 = 12% |
| Dedicated logic registers: | 1364 / 22320 = 6% |
| Total pins: | 18 |
| Total memory bits: | 297984 / 608256 = 49% |
| Embedded Multiplier 9-bit elements: | 2 / 132 = 2% |
| Maximum Frequency: | 99.11 MHz |
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
Application Software
Currently the Atlas 2k project includes only some example programs for the core:
- A simple blinking LED to get into the basics of the Atlas 2k assembler
- A random numbe rgenerator to play with the internal LFSR
- A Fast Fourier Transformation to impress you with the processing power... 😉
- ... more to come
,You have written some cool program for the Atlas 2k?
Get in touch so we can add your code to the examples collection to share it with the community!,
,
,
,
Status
- The main processor rtl modules are completed and tested - maybe additional coprocessor modules will be added
- Some of the rarely used special options of some commands need a little bit more verification... 😉
- The bootloader works fine can successfully boot an image from any source
- All example programs run without problems
- Processor specification completed, but might be updated with additional information in future
- Assembler program is working and will be further improved
- The 'Atlas 2k Base Setup' features a ready-to-start implementation of the processor - FPGA proven
,
,
Contact
If you have any questions about the Atlas project or if you want to give any kind of feedback, feel free to drop me some lines 😉
- Stephan Nolting: stnolting@gmail.com
,
Next step







